What are the key elements of sustainable home design? This question is at the forefront of modern architecture as we seek to create living spaces that harmonize with our environment. Sustainable home design emphasizes not only the aesthetic appeal of a building but also its ecological footprint. By focusing on aspects such as site selection, energy efficiency, and the use of sustainable materials, we can cultivate homes that are both functional and environmentally friendly.
The discussion around sustainable home design integrates various principles that aim to minimize environmental impact while promoting energy conservation and resource efficiency. As the world grapples with climate change, understanding these key elements becomes crucial for homeowners, builders, and architects alike.
Site Selection and Orientation

Choosing the right location for a sustainable home is a crucial step in the design process. The site selection not only affects the environmental impact of the construction but also plays a significant role in the long-term sustainability of the home. A well-chosen site can enhance energy efficiency, reduce resource consumption, and harmonize the dwelling with its surroundings, fostering a connection with nature.The orientation of a building significantly influences its energy efficiency.
Properly orienting a home can maximize natural light and harness solar energy, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and heating. For instance, positioning windows toward the south in the Northern Hemisphere can capture sunlight during the winter months while minimizing heat gain during the summer. This strategic orientation can lead to substantial reductions in energy costs and improve overall comfort for the inhabitants.
Staging your home effectively can significantly enhance its appeal to potential buyers. To achieve a quick sale, it’s essential to create an inviting atmosphere that showcases your property’s best features. You can discover valuable insights on how to stage my home for a quick sale that will help you optimize your space and make the right impression.
Site Features that Enhance Sustainability
When selecting a site for a sustainable home, various natural features can be leveraged to promote an environmentally friendly living space. Understanding these features can help in making informed decisions that align with sustainability goals. Key site features include:
- Natural Vegetation: Preserving existing trees and plants can provide shade, reduce heat islands, and enhance biodiversity. Mature trees can act as windbreaks, lowering heating costs in winter.
- Topography: Utilizing the natural slope of the land can facilitate drainage and prevent erosion. Building on elevated areas can also provide natural cooling breezes.
- Water Sources: Proximity to lakes, rivers, or ponds can offer opportunities for sustainability practices such as rainwater harvesting and natural irrigation systems.
- Soil Quality: Assessing the soil for its ability to support landscaping or gardens is fundamental. Healthy soil can contribute to increased food production and carbon sequestration.
- Wind Patterns: Analyzing prevailing winds can guide the placement of windows and openings to maximize cross-ventilation, thereby reducing the need for mechanical cooling.
By thoughtfully integrating these site features into the design and orientation of a sustainable home, architects and builders can create living spaces that are not only energy-efficient but also environmentally harmonious. This approach promotes a lifestyle that respects and nurtures the surrounding ecosystem while enhancing the quality of life for its occupants.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Sources
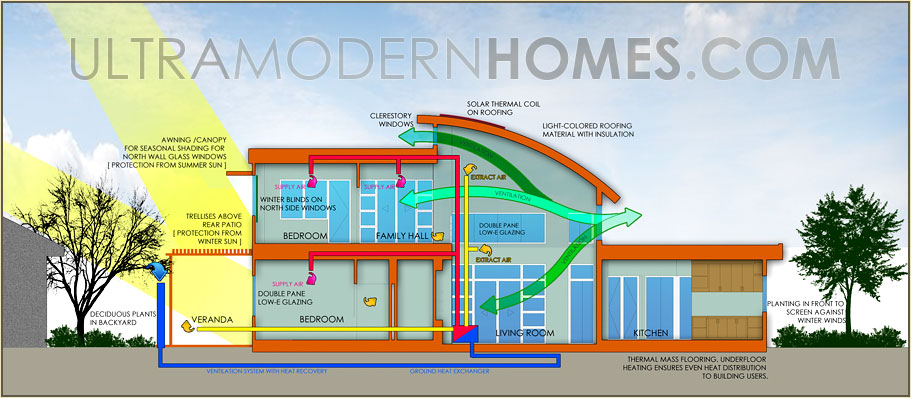
Incorporating energy efficiency and renewable energy sources into home design is essential for creating sustainable living environments. These elements not only reduce dependence on fossil fuels but also minimize the overall carbon footprint of residential buildings. A well-designed home can lead to significant energy savings, enhancing both economic and ecological benefits for the homeowners.Key components of energy-efficient home design include proper insulation, efficient windows and doors, and energy-efficient appliances.
Staging your home effectively is crucial for attracting potential buyers and ensuring a swift sale. A well-staged home not only highlights its best features but also allows buyers to envision themselves living there. To learn the best practices on how to stage my home for a quick sale , consider decluttering, enhancing curb appeal, and using neutral decor to create an inviting atmosphere.
These steps can significantly impact the selling process.
Each of these elements plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption by maintaining temperature, minimizing air leaks, and utilizing energy wisely. Moreover, integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines can further enhance a home’s sustainability.
Energy-Efficient Home Design Components
The foundation of an energy-efficient home lies in its design and construction. Key components contributing to this efficiency include:
- Insulation: High-quality insulation materials minimize heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, leading to reduced energy costs and improved comfort.
- Windows and Doors: Energy-efficient windows with low U-values and double or triple glazing prevent heat transfer, while well-sealed doors reduce drafts.
- Appliances: Energy Star-rated appliances use significantly less energy compared to standard models, further minimizing household energy consumption.
- Lighting: Utilizing LED or fluorescent lighting provides better efficiency and longevity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
Incorporation of Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of renewable energy sources is vital for achieving a sustainable home. Common methods to incorporate these technologies include:
- Solar Panels: Installing photovoltaic systems enables homes to generate their own electricity from sunlight, significantly reducing reliance on grid energy.
- Wind Turbines: For properties with adequate land and wind resources, small-scale wind turbines can produce renewable energy, diversifying energy sources.
- Geothermal Systems: Utilizing the earth’s stable underground temperature for heating and cooling systems can greatly enhance energy efficiency.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Capturing and utilizing rainwater for irrigation or non-potable uses can reduce water consumption and energy used in water treatment.
Passive Design Strategies
Passive design strategies focus on maximizing natural resources to maintain comfort while minimizing energy use. Essential strategies include:
- Orientation: Positioning a home to take advantage of natural sunlight can significantly reduce heating needs during winter and cooling loads in summer.
- Thermal Mass: Materials that absorb and store heat can help regulate indoor temperatures, minimizing the need for mechanical heating and cooling.
- Natural Ventilation: Designing for cross-ventilation helps cool the home naturally, reducing reliance on air conditioning systems.
- Landscaping: Strategic placement of trees and shrubs can provide shade and wind protection, further decreasing heating and cooling demands.
“By embracing energy-efficient designs and renewable energy sources, homeowners can create spaces that not only conserve resources but also contribute to a healthier planet.”
Sustainable Materials and Resources

Selecting sustainable materials is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of home construction. Sustainable materials minimize waste, conserve energy, and enhance the overall health and comfort of living spaces. This section delves into the criteria for selecting sustainable building materials, highlights eco-friendly materials and their benefits, and discusses methods for recycling and repurposing materials in home construction.
Criteria for Selecting Sustainable Building Materials
The selection of sustainable building materials is guided by several key criteria that ensure the materials contribute positively to the environment and human health. These criteria include:
- Renewability: Materials should be derived from renewable resources or processes that regenerate naturally, such as bamboo or reclaimed wood.
- Resource Efficiency: The extraction and processing of materials should minimize energy consumption and environmental degradation. Materials with low embodied energy are preferred.
- Toxicity: Select materials that are non-toxic and do not emit harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), ensuring better indoor air quality.
- Durability: Sustainable materials should have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, reducing the need for replacements and repairs.
- Recyclability: Materials should be recyclable at the end of their life cycle, promoting a circular economy and reducing landfill waste.
Examples of Eco-Friendly Materials and Their Benefits
A variety of eco-friendly building materials are available, each offering distinct advantages that contribute to sustainable home design. Notable examples include:
- Recycled Steel: Provides strength and durability; using recycled steel reduces the need for mining and conserves natural resources.
- Straw Bale: Offers excellent insulation properties and is a renewable resource, making it a cost-effective and energy-efficient option.
- Hempcrete: A lightweight and biodegradable material that provides thermal insulation and absorbs CO2, helping to reduce greenhouse gases.
- Low-VOC Paints: Enhance indoor air quality by minimizing harmful emissions, while still offering a wide range of colors and finishes.
- Reclaimed Wood: Utilizes old wood from buildings and furniture, reducing waste and providing unique character and history to new constructions.
Methods for Recycling and Repurposing Materials
Incorporating recycling and repurposing into home construction not only conserves resources but also adds unique elements to a design. Effective methods for recycling and repurposing materials include:
- Deconstruction: Instead of demolition, deconstructing a building allows for the salvage of valuable materials such as bricks, wood, and fixtures for reuse.
- Upcycling: Creative reuse of materials, such as transforming old doors into tables or using pallets for furniture, can enhance aesthetic value while reducing waste.
- Material Recovery Facilities: Partnering with local facilities that specialize in recovering and recycling construction waste can facilitate the responsible disposal and reuse of materials.
- Community Exchange Programs: Engaging in local exchanges where homeowners can donate surplus materials can benefit the community while promoting sustainable practices.
Water Conservation and Management: What Are The Key Elements Of Sustainable Home Design
Water conservation is a critical component of sustainable home design, aiming to reduce water usage and minimize the environmental impact of water consumption. Given the growing concerns surrounding water scarcity and its management, it becomes essential for homeowners and developers to incorporate water-efficient systems into their designs. By focusing on innovative water management strategies, individuals can contribute to long-term sustainability and promote responsible water use in their households.The significance of water-efficient fixtures and appliances cannot be understated in the pursuit of sustainable home design.
These fixtures, such as low-flow faucets, toilets, and showerheads, significantly reduce water consumption without sacrificing performance. The use of energy-efficient dishwashers and washing machines also plays a crucial role in minimizing water waste. For instance, a WaterSense-labeled toilet can save an average of 13,000 gallons of water per year compared to older models. This not only preserves a vital resource but also results in substantial savings on water bills, making it a financially viable choice for homeowners.
Rainwater Harvesting and Greywater Recycling Systems, What are the key elements of sustainable home design
Implementing rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling systems can greatly enhance water conservation efforts in residential settings. Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater from rooftops for various non-potable uses, such as irrigation and toilet flushing. This practice not only reduces reliance on municipal water supply but also helps in managing stormwater runoff, thereby reducing the risk of flooding and erosion.
In addition, greywater recycling systems capture water from sinks, showers, and laundry, which can then be reused for irrigation or flushing toilets. By diverting this otherwise wasted water, homeowners can significantly reduce their overall water consumption. A well-designed greywater system can conserve thousands of gallons of water annually, offering both environmental and economic benefits.
Landscaping Techniques for Water Conservation
Employing landscaping techniques that promote water conservation is another crucial aspect of sustainable home design. Xeriscaping, a landscaping method that emphasizes drought-resistant plants and efficient irrigation practices, is an effective strategy to reduce water use in gardens and yards. By selecting native plants that thrive in the local climate, homeowners can minimize the need for supplemental watering, thereby conserving water.Additionally, the use of mulch can help maintain soil moisture and reduce evaporation, while drip irrigation systems provide water directly to the plant roots, ensuring efficient use of water resources.
Implementing these landscaping techniques not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of a home but also contributes to sustainable water management practices.